Elastomeric Materials
ELASTOMERIC MATERIALS
ELASTOMERIC MATERIALS IS ANY MATERIAL EXHIBITING ELASTIC OR RUBBER-LIKE PROPERTIES.
Elastomeric materials are measured in material type, compound, and durometer (the material’s hardness).
Since there is such a wide variety of elastomeric materials, the application is critical to understanding the job’s best material compound.
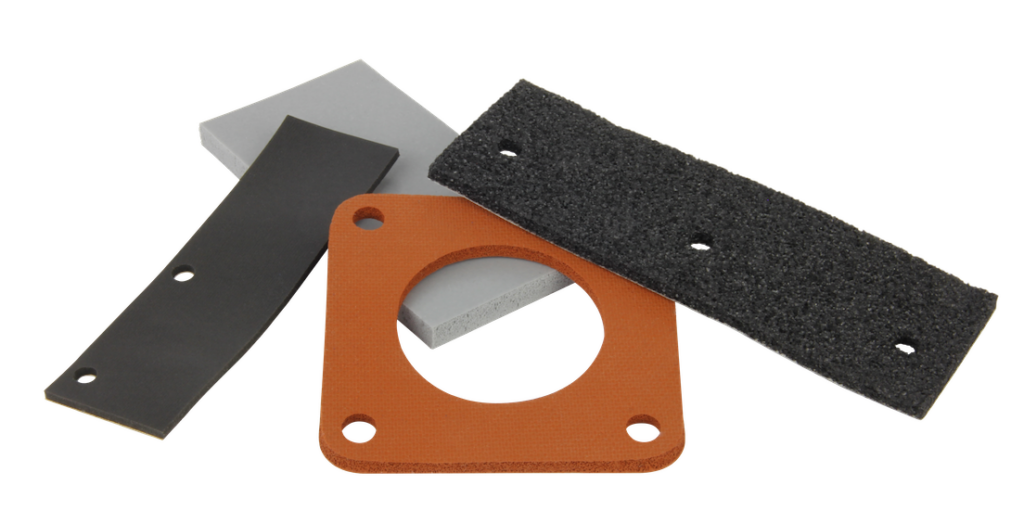
FOAM / SPONGE
FOAM AND SPONGE ARE GENERALLY GROUPED AND REGARDED AS IN THE SAME PLASTIC/ELASTOMERIC MATERIALS FAMILY BECAUSE THEY EXHIBIT THE SAME CELLULAR STRUCTURE.
Additionally, they are commonly listed under similar industry specifications (ASTM, MIL, UL, FMVSS, and others).
Foam is a lightweight, open-cell product that is typically used for insulation, filtration, and cushioning. These low density cellular materials allow air movement through the cell structure. In addition to traditional foam’s legacy applications, high-density foams have been developed for fluid-sealing applications. In contrast, higher-density foam products will have a higher concentration of cells. Medium and low-density foams will have a lower concentration of cells.
The sponge is an expanded, rubber-based material. The sponge can be processed in multiple material formulations (different compounds, densities, or open and closed cellular structures). The cells are not connected, which keeps the material from absorbing and retaining liquid. Compared to foams, sponges are considered to have superior mechanical properties.
Sponge and foam are available in sheets, rolls, and molded or extruded shapes. As needed, they can be ordered with or without ‘skin’ and PSAs (pressure-sensitive adhesive).
COMMON BRANDS:
- Rogers
- Monmouth
- Armacel
- K-Flex
- Rubatex
- Griswold
COMMON TRADE NAMES:
- Poron
- Bisco
- EnsoLite®

USES:
- Filtration
- Thermal Insulation
- Cushioning
- Padding
- Gaskets
- Weather Stripping
- Sound Barrier
To learn more about foam and sponge elastomeric materials from The Gund Company or request a quote for your application, Contact Us Today!
| SPONGE SPECIFICATION GUIDE | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymer | NEO/EPDM/SBR | EPDM/BLEND | EPT BLEND | |||||
| Specification | ||||||||
| ASTM D1056-67 | SCE41 | SCE42 | SCE43 | SCE45 | RE41E | RE42E | RE43E | RE41EPT |
| ASTM D1056-07 | 2A1 | 2A2 | 2A3 | 2A5 | 2A1 | 2A2 | 2A3 | 2A1 |
| MIL-R-6130 TYP + ASTM D6576 | II-A | II-A | II-A | II-A | II-B | II-B | II-B | —– |
| GRADE CONDITION | Soft | Soft-Med | Medium | Firm | Soft | Soft-Med | Medium | —– |
| MIL-C-3133C MIL STD 6708 | SCE3 F2 | SCE7 F2 | SCE11 F2 | SCE20 F2 | RE3 F2 | RE7 F2 | RE11 F2 | RE3 |
| FLAMMABILITY SPECIFICATION | ||||||||
| UL94 HF1 | Listed | Listed | Listed | —– | —– | —– | —– | —– |
| UL94 HBF | Listed | Listed | Listed | —– | —– | —– | —– | —– |
| MIL-R-6130C | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | —– |
| FMVSS-302 | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | —– |
| PHYSICAL PROPERTIES | ||||||||
| 25% Compression Deflection [psi] | 2-5 | 5-9 | 9-13 | 17-25 | 2-5 | 5-9 | 9-13 | 2-5 |
| Density Approximate [pcf] | 6 +/-2 | 6 +/-2 | 9 +/-2 | 12 +/-2 | 6 +/-2 | 6 +/-2 | 9 +/-2 | 4 +/-1 |
| Water Absorption Max. Weight % | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Temperature Range oF | -40/+200 | -40/+200 | -40/+200 | -40/+150 | -70/+220 | -70/+220 | -70/+220 | -40/+200 |
| Temperature High Intermittent oF | 250 | 250 | 250 | 200 | 250 | 250 | 250 | 250 |
| Ozone Resistance | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent | Fair | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
| Tensile Strength [psi] | 75 | 100 | 100 | 150 | 75 | 75 | 100 | 40 |
| Fuel B Max. % Weight Change | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Elongation Typical Properties % | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 175 |
| Durometer Shore 00 [Approx.] | 40-50 | 45-55 | 55-65 | 65-75 | 40-50 | 45-55 | 55-65 | 37-47 |
| Shrinkage 7 Days @ 158o Max. | 5% | 5% | 5% | 5% | 5% | 5% | 5% | 5% |
| K Factor | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.38 | —– | 0.3 | 0.30 | 0.38 | 030 |
| Polymer | 100% NEOPRENE | EVA | PVC/NITRILE | |||||
| Specification | ||||||||
| ASTM D1056-67 | SCE41NEO | SCE42NEO | 2#EVA | 4#EVA | IV1 | IV2 | IV3 | |
| ASTM D1056-07 | 2C1 | 2C2 | 2A1/2A2 | 2A2/2A3 | 2C1 | 2C2 | 2B3 | |
| MIL-R-6130 TYP + ASTM D6576 | II-A | II-A | —– | —– | 11-B | 11-A/B | 11-A/B | |
| GRADE CONDITION | Soft | Soft-Med | —– | —– | Soft | Soft-Med | Medium | |
| MIL-C-3133C MIL STD 6708 | SCE3 F1 | SCE7 F1 | —– | —– | SCE3 | SCE7 | SCE11 | |
| FLAMMABILITY SPECIFICATION | ||||||||
| UL94 HF1 | Pass | Pass | —– | —– | Listed | Listed | Listed | |
| UL94 HBF | Pass | Pass | —– | —– | Pass | Pass | Pass | |
| MIL-R-6130C | Pass | Pass | —– | —– | Pass | Pass | Pass | |
| FMVSS-302 | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | |
| PHYSICAL PROPERTIES | ||||||||
| 25% Compression Deflection [psi] | 2-5 | 5-9 | 4-6 | 9-13 | 2-5 | 5-9 | 9-13 | |
| Density Approximate [pcf] | 9 +/-2 | 9 +/-2 | 2 +/-5 | 3.0-4.0 | 3.0-5.0 | 5.5-7.5 | 7.0-9.5 | |
| Water Absorption Max. Weight % | 5 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 7 | 5 | 5 | |
| Temperature Range oF | -40/+150 | -40/+150 | -110/+220 | -110/+220 | -40/+200 | -40/+200 | -40/+200 | |
| Temperature High Intermittent oF | 200 | 200 | 240 | 240 | 225 | 225 | 225 | |
| Ozone Resistance | Fair | Fair | Excellent | Excellent | Fair | Fair | Fair | |
| Tensile Strength [psi] | 80 | 90 | 60 | 100 | 50 | 75 | 100 | |
| Fuel B Max. % Weight Change | <250 | <250 | n/a | n/a | <250 | <250 | <100 | |
| Elongation Typical Properties % | 150 | 150 | 275 | 310 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| Durometer Shore 00 [Approx.] | 45-55 | 50-60 | —– | —– | 30-45 | 50-60 | 60-70 | |
| Shrinkage 7 Days @ 158o Max. | 5% | 5% | 5% | 5% | 3% | 3% | 3% | |
| K Factor | 0.38 | 0.38 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.25 | 0.23 | 0.30 | |
| Polymer | Closed Cell Silicone Sponge | |||||||
| Specification | ||||||||
| AMS | 3195 | 3196 | ||||||
| MIL | MIL-R-46089 | MIL-R-46089 | ||||||
| DENSITY | ||||||||
| PHYSICAL PROPERTIES | Soft | Medium | Firm | Extra-Firm | ||||
| 25% Compression Deflection [psi] | 5-9 | 6-14 | 12-20 | 16-28 | ||||
| Density Approximate [pcf] | 31 | 33 | 40 | 45 | ||||
| Water Absorption Max. Weight % | <1% | <1% | <1% | <1% | ||||
| Temperature Range oF | -103 / +450 | -103 / +450 | -103 / +450 | -103 / +450 | ||||
| Temperature High Intermittent oF | ||||||||
| Ozone Resistance | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent | ||||
| Tensile Strength [psi] | Good | Good | Very Good | Very Good | ||||
| Elongation Typical Properties % | Good | Good | Very Good | Excellent | ||||
| Thermal Conductivity BTU | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.80 | 0.85 | ||||
| in/hr/ft3/oF | ||||||||
| Dielectric Strength [approx] | 150 volts/mil | 150 volts/mil | 150 volts/mil | 150 volts/mil | ||||
RUBBER
RUBBER IS OFTEN REFERRED TO AS A “SOLID ELASTOMERIC MATERIALS.” GENERALLY SPEAKING, THE TWO MOST COMMON TYPES OF RUBBER ARE NATURAL AND SYNTHETIC. NATURAL (GUM) RUBBERS ARE DERIVED FROM THE RUBBER TREE.
Conversely, rubber-like materials produced from sources other than the rubber tree are commonly referred to as synthetic rubber.
Though there are currently more than 36 synthetic rubber compounds available, not all are commonly used. Rubber compounds have been researched, developed, and engineered to meet many application requirements, including fluid, temperature, and pressure resistance. Many synthetic rubber elastomeric materials are also available with different degrees of reinforcement, such as cloth inserted (CI) of fabric reinforced (diaphragm).
COMMON TRADE NAMES:
- Nitrile [Buna-N]
- Neoprene
- Silicone
- FKM [Viton®]
- EPDM
- SBR
- Fluorosilicone
- and many more.
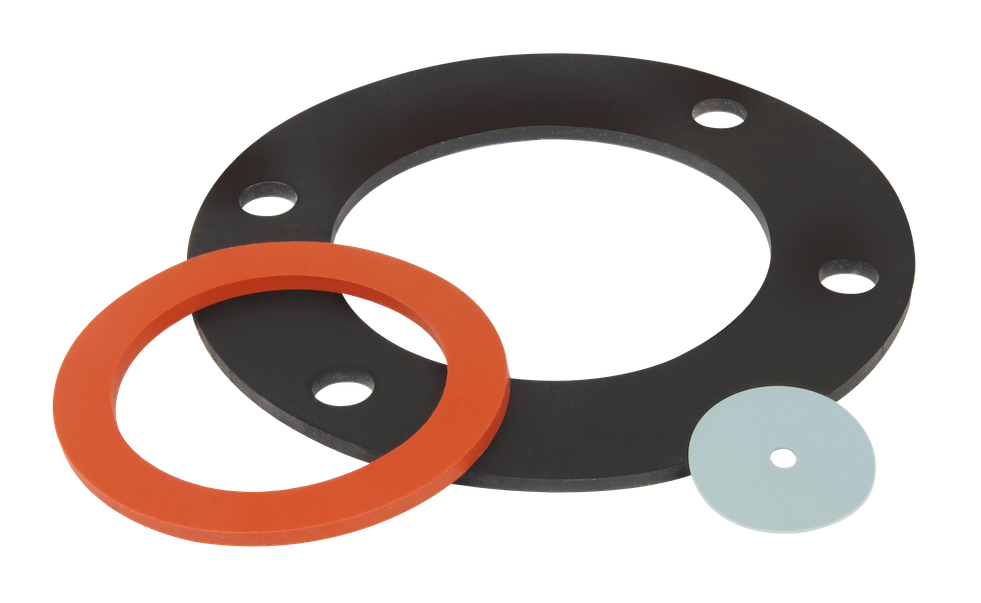
COMMON USES:
- Gaskets
- Diaphragms
- Seals
- Chute Lining
- Seats
- Extrusions
- Door Seals
- Molded Seals [Shapes]
- Tubing
- Bumpers
- Pads
- Grommets
- Washers
| POLYMER CHARACTERISTICS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymers | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber | Ethylene Propylene | Fluoroelastomer | Silicone |
| Common Names | Buna-N, Nitrile, NBR | EPR, EPT, EP, EPDM | Viton®, FKM | VMQ |
| ASTM D1418 Designation | NBR | EPDM, EPM | FKM | Q, MQ, PMQ, PVMQ |
| ASTM D2000 Type/Class | BF, BG, BK, CH | AA, BA, CA, DA | HK | FC, FE, GE |
| Mil-R-3065 [Mil-Std-417 Class | SB | RS | TB | TA |
| General Characteristics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Durometer Range [Shore A] | 20-95 | 30-90 | 50-95 | 10-85 |
| Tensile Range [psi] | 200-3500 | 500-2500 | 500-2000 | 500-2500 |
| Elongation Range % | 350-650 | 100-700 | 400-500 | 450-900 |
| Compression Set Resistance | Good to Excellent | Good | Good to Excellent | Excellent |
| Resilience / Rebound | Good to Excellent | Fair to Good | Poor to Fair | Good |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good to Excellent | Good | Fair to Good | Good |
| Tear Strength | Good to Excellent | Fair to Good | Fair to Good | Good |
| Solvent Resistance | Good to Excellent | Poor | Excellent | Poor |
| Oil Resistance | Excellent | Poor | Excellent | Poor |
| Low Temperature oF | -70 | -60 | -30 | -75 |
| High Temperature oF | +250 | +300 | +572 | +500 |
| Ozone Resistance | Fair to Good | Good to Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
| Polymers | Polychloroprene | Styrene Butadiene Rubber | Fluorosilicone | Polyisobutylene |
| Common Names | Neoprene | SBR | FVMQ | Butyl |
| ASTM D1418 Designation | CR | SBR | FVMQ | IIR, BIIR, CIIR |
| ASTM D200 Type/Class | BA, BC | AA, BA | FK | AA, BA |
| Mil-R-3065 [Mil-Std-417 Class | SE | RS | TA | RS |
| General Characteristics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Durometer Range [Shore A] | 20-95 | 30-95 | 40-80 | 40-90 |
| Tensile Range [psi] | 500-3000 | 500-2900 | 500-1500 | 500-2900 |
| Elongation Range % | 100-800 | 300-450 | 150-600 | 300-850 |
| Compression Set Resistance | Poor to Good | Good to Excellent | Very Good | Fair to Good |
| Resilience / Rebound | Fair to Good | Good | Good | Fair to Good |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good to Excellent | Excellent | Poor | Fair to Good |
| Tear Strength | Good to Excellent | Fair to Excellent | Poor | Good |
| Solvent Resistance | Fair | Poor | Excellent | Poor |
| Oil Resistance | Fair | Poor | Good | Poor |
| Low Temperature oF | -70 | -60 | -100 | -70 |
| High Temperature oF | +250 | +250 | +450 | +300 |
| Ozone Resistance | Good to Excellent | Poor to Good | Excellent | Excellent |
To learn more about rubber elastomeric materials from The Gund Company or request a quote for your application, Contact Us Today!
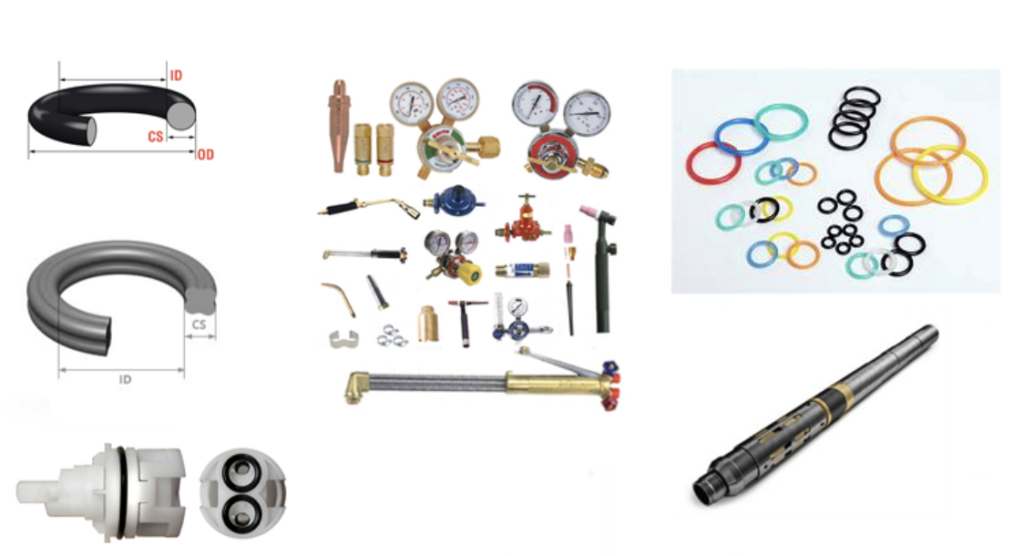
O-RINGS
O-RINGS’ PRIMARY FUNCTIONS ARE TO CREATE A BARRIER BETWEEN TWO ITEMS WHERE AIR OR FLUID MAY ESCAPE.
They are typically installed in a groove to hold them in place while squeezed between two opposite surfaces. In most cases, O-rings are sized using the inside diameter (ID) by Cross Section (CS). O-rings are particularly effective because they have memory and want to expand to their original size and shape. So compressing them between two opposing surfaces creates an air and/or fluid-tight seal. O-rings are available in a variety of natural and synthetic rubber compounds. Depending on the application, the material chosen can significantly impact the functionality of the O-ring.
Though they are a common commodity, choosing the proper O-ring for the application can be challenging when considering thermal resistance and degradation from fluid and gases. Additionally, there are several standards for O-rings worldwide. The most common standard for North America is AS568. We understand the various mechanical properties of O-ring materials. Contact one of our material specialists today to review your applications or request a quote.
O-rings are available in most polymer compounds and sizes, including AS568B [chart below], metric sizes, both molded and vulcanized endless from the O-ring cord.
APPLICATIONS:
- Hydraulics
- Faucets
- Gaskets
- Setting Tools
- Frac Plugs
- Carburetors
- Gas Valves
- Helicopters

| Cross Section | Cross Section | Cross Section | |||||||||||||
| 1/16 | 3/32 | 1/8 | 3/16 | 1/16 | 3/32 | 1/8 | 3/16 | 1/4 | 3/32 | 1/8 | 3/16 | 1/4 | |||
| ID | (.070) | (.103) | (.139) | (.210) | ID | (.070) | (.103) | (.139) | (.210) | (.275) | ID | (.103) | (.139) | (.210) | (.275) |
| 1/32 | 001* | 2 3/16 | 139 | 7 | 167 | 262 | 365 | 441 | |||||||
| 3/64 | 002* | 2 1/4 | 053 | 140 | 228 | 331 | 7 1/4 | 168 | 263 | 366 | 442 | ||||
| 1/16 | 003 | 102 | 2 5/16 | 141 | 7 1/2 | 169 | 264 | 367 | 443 | ||||||
| 5/64 | 004 | 2 3/8 | 036 | 142 | 229 | 332 | 7 3/4 | 170 | 265 | 368 | 444 | ||||
| 3/32 | 005 | 103 | 2 7/16 | 143 | 8 | 171 | 266 | 369 | 445 | ||||||
| 1/8 | 006 | 104 | 2 1/2 | 037 | 144 | 230 | 333 | 8 1/4 | 172 | 267 | 370 | ||||
| 5/32 | 007 | 105 | 2 9/16 | 145 | 8 1/2 | 173 | 268 | 371 | 446 | ||||||
| 3/16 | 008 | 106 | 201 | 2 5/8 | 038 | 146 | 231 | 334 | 8 3/4 | 174 | 269 | 372 | |||
| 7/32 | 009 | 107 | 2 11/16 | 147 | 9 | 175 | 270 | 373 | 447 | ||||||
| 1/4 | 010 | 108 | 202 | 2 3/4 | 039 | 148 | 232 | 335 | 9 1/4 | 175 | 271 | 374 | |||
| 5/16 | 011 | 109 | 203 | 2 13/16 | 149 | 9 1/2 | 177 | 272 | 375 | 448 | |||||
| 3/8 | 012 | 110 | 204 | 2 7/8 | 040 | 150 | 233 | 336 | 9 3/4 | 178 | 273 | 376 | |||
| 7/16 | 013 | 111 | 205 | 309 | 3 | 041 | 151 | 234 | 337 | 10 | 274 | 377 | 449 | ||
| 1/2 | 014 | 112 | 206 | 310 | 3 1/8 | 235 | 338 | 10 1/2 | 275 | 378 | 450 | ||||
| 9/16 | 015 | 113 | 207 | 311 | 3 1/4 | 042 | 152 | 236 | 339 | 11 | 276 | 379 | 451 | ||
| 5/8 | 016 | 114 | 208 | 312 | 3 3/8 | 237 | 340 | 11 1/2 | 277 | 380 | 452 | ||||
| 11/16 | 017 | 115 | 209 | 313 | 3 1/2 | 043 | 153 | 238 | 341 | 12 | 278 | 381 | 453 | ||
| 3/4 | 018 | 116 | 210 | 314 | 3 5/8 | 239 | 342 | 12 1/2 | 454 | ||||||
| 13/16 | 019 | 117 | 211 | 315 | 3 3/4 | 044 | 154 | 240 | 343 | 13 | 279 | 382 | 455 | ||
| 7/8 | 020 | 118 | 212 | 316 | 3 7/8 | 241 | 344 | 13 1/2 | 456 | ||||||
| 15/16 | 021 | 119 | 213 | 317 | 4 | 045 | 155 | 242 | 345 | 14 | 280 | 383 | 457 | ||
| 1 | 022 | 120 | 214 | 318 | 4 1/8 | 243 | 346 | 14 1/2 | 458 | ||||||
| 11/16 | 023 | 121 | 215 | 319 | 4 1/4 | 046 | 156 | 244 | 347 | 15 | 281 | 384 | 459 | ||
| 11/8 | 024 | 122 | 216 | 320 | 4 3/8 | 245 | 348 | 15 1/2 | 460 | ||||||
| 13/16 | 025 | 123 | 217 | 321 | 4 1/2 | 047 | 157 | 246 | 349 | 425 | 16 | 282 | 385 | 461 | |
| 11/4 | 026 | 124 | 218 | 322 | 4 5/8 | 247 | 350 | 426 | 16 1/2 | 462 | |||||
| 15/16 | 027 | 125 | 219 | 323 | 4 3/4 | 048 | 158 | 248 | 351 | 427 | 17 | 283 | 386 | 463 | |
| 13/8 | 028 | 126 | 220 | 324 | 4 7/8 | 249 | 352 | 428 | 17 1/2 | 464 | |||||
| 17/16 | 127 | 221 | 5 | 049 | 159 | 250 | 353 | 429 | 18 | 284 | 387 | 465 | |||
| 11/2 | 029 | 128 | 222 | 325 | 5 1/8 | 251 | 354 | 430 | 18 1/2 | 466 | |||||
| 19/16 | 129 | 5 1/4 | 050 | 160 | 252 | 355 | 431 | 19 | 388 | 467 | |||||
| 15/8 | 030 | 130 | 223 | 326 | 5 3/8 | 253 | 356 | 432 | 19 1/2 | 468 | |||||
| 1 11/16 | 131 | 5 1/2 | 161 | 254 | 357 | 433 | 20 | 389 | 469 | ||||||
| 13/4 | 031 | 132 | 224 | 327 | 5 5/8 | 255 | 358 | 434 | 21 | 390 | 470 | ||||
| 1 13/16 | 133 | 5 3/4 | 162 | 256 | 359 | 435 | 22 | 391 | 471 | ||||||
| 17/8 | 032 | 134 | 225 | 328 | 5 7/8 | 257 | 360 | 436 | 23 | 392 | 472 | ||||
| 1 15/16 | 135 | 6 | 163 | 258 | 361 | 437 | 24 | 393 | 473 | ||||||
| 2 | 033 | 136 | 226 | 329 | 6 1/4 | 164 | 259 | 362 | 438 | 25 | 394 | 474 | |||
| 2 1/16 | 137 | 6 1/2 | 165 | 260 | 363 | 439 | 26 | 395 | 475 | ||||||
| 2 1/8 | 034 | 138 | 227 | 330 | 6 3/4 | 166 | 261 | 364 | 440 | ||||||
*Section Diameter of AS568-001 is 1/32
* Sectional diameter of AS568-002 is 3/64
To learn more about O-Ring materials from The Gund Company or request a quote for your application, Contact Us Today!
EMI SHIELDING / THERMAL MANAGEMENT
EMI SHIELDING AND THERMAL MANAGEMENT ARE GENERALLY GROUPED. THEY ARE COMMONLY LISTED UNDER SIMILAR INDUSTRY SPECIFICATIONS.
EMI Shielding: Electromagnetic Interference has become far more significant in recent years as the use of electronic devices continues to increase. As the utilization of these devices continues to grow, so does the exposure to a wide range of frequencies. Through years of research and development, manufacturers have determined that electrical insulation, enclosures, and cables have proven to be effective ways to contain these frequencies.
Organizations such as the CE & FCC have provided guidelines in the form of legal requirements to prevent electromagnetic interference (noise). Because of that. EMI Shielding has become a necessity in the electronics industry. Since there is a wide variety of application designs and frequency requirements, various materials have been developed to provide adequate shielding.
Thermal Management: Historically, thermal grease was used to create continuity between power sources and heat sinks. Unfortunately, this grease was not ideal in applications where ease of installation and cleanliness were paramount. These days, many applications utilize thermally-conductive materials or thermal management in place of this grease.
Thermally-conductive compounds contain fillers that maintain flexibility in service while providing continuity between the mating surfaces. In electronic equipment, air acts as an insulator and must be eliminated for optimum performance. Manufacturers of electronic devices want to establish an anaerobic environment to allow continuity between the power source and heat sink for proper performance. Such thermal management products create continuity within the component to optimize the heat dissipation from the power source.
Thermal management products are used in an expansive list of applications. And so, there is an equally wide variety of thermal management options available.
The Gund Company is well versed in both EMI Shielding and Thermal Management Contact one of our material specialists today to review your applications or request a quote.

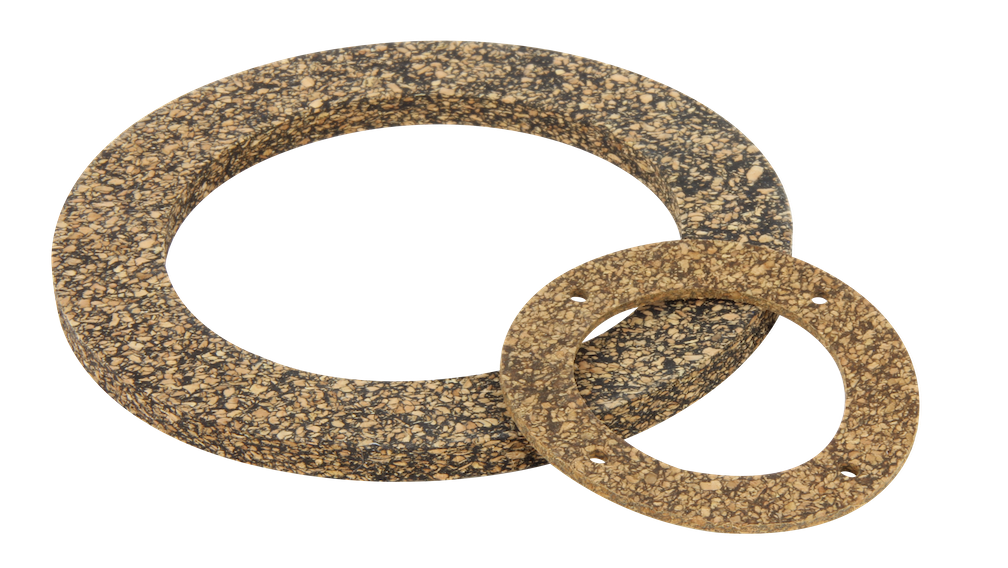
CORK / RUBBER
CORK & RUBBER PRODUCTS ARE INSTRUMENTAL IN METAL-TO-METAL JOINTS.
No allowance needs to be made for the side flow if a proper firmness material is selected. The compressibility of cork/rubber can be used in place of more expensive non-compressible rubber seals. Some of the friction of cork is retained in these products and helps to reduce extrusion and slippage.
Cork/rubber products can contain sponged materials that conform to and compensate for minor flange irregularities more easily. This characteristic is especially useful in stamped or other lightweight assemblies where the available bolt spacing and bolt load are usually low.
Cork/rubber products have an unusual resilience which helps resist compression set and other effects of fatigue. Cork-rubber seals are more resistant to aging than traditional rubber compounds.
Cork/rubber compounds are used to establish and maintain intimate contact between the flanges. The most common synthetic rubber compounds are Neoprene® and Nitrile. However, special applications may use cork material blended with Hypalon®, Silicone, Fluoroelastomer, SBR, or Vamac.
COMMON BRANDS:
- ECORE Intl
- Amorim Cork Solutions
COMMON TYPES:
- Composition Cork
- Cork & Neoprene
- Cork & Nitrile
- Cork & Sponged Rubber

| Cork & Rubber Composition | |||||
| Property | Test Method | Typical Result | Typical Result | Typical Result | Typical Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymer | Neoprene | Neoprene | Nitrile | EPDM – Sponge | |
| Density [ibs/ft3] | ASTM D3676 | 35.7 | 37.5 | 39.9 | 31.5 |
| Tensile Strength [lbs/in2] | ASTM F152 | 240 | 355 | 253 | 135 |
| Compression @ 100 psi | ASTM F36 | —- | —- | —- | 35% |
| Compression @ 400 psi | ASTM F36 | 45% | 29% | 40% | —- |
| Recovery | 80% | 80% | 82% | 90% | |
| Shore A Hardness | ASTM D2240 | 63 | 60 to 80 | 60 to 70 | 54 |
| Flexibility | ASTM F147 | 3 max | 3 max | 3 max | 3 max |
| Fluid Immersion | ASTM F146 | ||||
| Oil 1 [70 hrs @ 212oF] | -5 to +15% | -10 to +8% | -5 to +10% | -10 to +10% | |
| Oil 3 {70 hrs @ 212oF] | +5 to +50% | +5 o 15% | —- | +15 to +50% | |
| Fuel A [22 hrs @ 75oF] | 0 to +35% | 0 to +15% | —- | 0 to +25% | |
| Compression Set B | ASTM D395 | ||||
| 25% deflection, 22 hrs @ 158oF | 55% max | 65% max | 60% max | 90% max | |
| Temperature Range oF | -140 to +250 | -140 to +250 | -140 to +250 | -140 to +250 | |
| Specification | ASTM F104 | F227000 M1 T | F226000 M2 T | F227000 M2 T | F226000 M1 T |
| Specification | MIL-G-12803 | P2255B | P2245A | P2256A | P2265A |
| Shelf Life | 5 Years | 5 Years | 5 Years | 5 Years | |
| Cork & Nitrile Composition | |||||
| Property | Test Method | Typical Result | Typical Result | Typical Result | Typical Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymer | Nitrile | Nitrile | Nitrile | Nitrile | |
| Density [ibs/ft3] | ASTM D3676 | 40.1 | 45.9 | 52.6 | 30.5 |
| Tensile Strength [lbs/in2] | ASTM F152 | 295 | 325 | 422 | 120 |
| Compression @ 100 psi | ASTM F36 | 25% | —– | —– | 38% |
| Compression @ 400 psi | ASTM F36 | 39% | 33% | 24% | |
| Recovery | 81% | 82% | 81% | 90% | |
| Shore A Hardness | ASTM D2240 | 60 to 75 | 60 to 75 | 60 to 80 | 50 |
| Flexibility | ASTM F147 | 3 max | 3 max | 3 max | 3 max |
| Fluid Immersion | ASTM F146 | ||||
| Oil 1 [70 hrs @ 212oF] | -5 to +10% | -5 to +10% | -5 to +10% | 0 to +15% | |
| Oil 3 {70 hrs @ 212oF] | -2 to +15% | -2 to +20% | -2 to +15% | +10 to +30% | |
| Fuel A [22 hrs @ 75oF] | -2 to +10% | -2 to +10% | -2 to +10% | 0 to +15% | |
| Compression Set B | ASTM D395 | ||||
| Cork & Neoprene Composition | |||||
| Property | Test Method | Typical Result | Typical Result | Typical Result | Typical Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymer | Neoprene | Neoprene | Neoprene | Neoprene | |
| Density [ibs/ft3] | ASTM D3676 | 35.6 | 48.4 | 53.1 | 48.4 |
| Tensile Strength [lbs/in2] | ASTM F152 | 218 | 336 | 400 | 336 |
| Compression @ 100 psi | ASTM F36 | —– | —– | —– | |
| Compression @ 400 psi | ASTM F36 | 47% | 25% | 26% | 32% |
| Recovery | 81% | 83% | 80% | 83% | |
| Shore A Hardness | ASTM D2240 | 61 | 65 to 75 | 60 to 80 | 65 to 75 |
| Flexibility | ASTM F147 | 3 max | 3 max | 3 max | 2 max |
| Fluid Immersion | ASTM F146 | ||||
| Oil 1 [70 hrs @ 212oF] | -2 to +10% | -2 to +20% | -2 to +20% | +2 to +10% | |
| Oil 3 {70 hrs @ 212oF] | +5 to +30% | +15 to +50% | +15 to +50% | +10 to +50% | |
| Fuel A [22 hrs @ 75oF] | 0 to +15% | 0 to +15% | 0 to +15% | 0 to +15% | |
| Compression Set B | ASTM D395 | ||||
| 25% deflection, 22 hrs @ 158oF | 60% max | 60% max | 55% max | 60% max | |
| Temperature Range oF | -40 to +250 | -40 to +250 | -40 to +250 | -40 to +250 | |
| Specification | ASTM F104 | —– | F226000 M2 T | F224000 M2 T | F226000 M2 T |
| Specification | MIL-G-12803 | —– | P2255A | P2254A | P2255A |
| Specification | AMS-C-6183 | TYP 1 CL 2 GR A | TYP 1 CL 2 GR B | TYP 1 CL 2 GR C | TYP 1 CL 2 GR B |
| Shelf Life | 5 Tears | 5 Tears | 5 Tears | 5 Tears | |
| Composition Cork | ||
| Property | Typical Result | |
|---|---|---|
| Density [ibs/ft3] | ASTM D3676 | 15.8 |
| Tensile Strength [lbs/in2] | ASTM F152 | 125 |
| Compression @ 100 psi | ASTM F36 | 36% |
| Recovery | 83% | |
| Flexibility | ASTM F147 | 5 max |
| Specification | ASTM F104 | F217000RT |
| Specification | MIL-G-12803 | P2128A |
| Specification | HH-C-576B | Cl 1 TY II |
To learn more about cork/rubber elastomeric materials from The Gund Company or request a quote for your application, Contact Us Today!
FELT / WOOL
NATURAL WOOL FELT IS ONE OF THE OLDEST MAN-MADE TEXTILES. MANY CULTURES HAVE LEGENDS AS TO HOW THE FELTING PROCESS WAS DISCOVERED.
One of the earliest accounts of felting details how nomads fleeing persecution packed their sandals with wool to prevent blisters while crossing the desert. At the end of their journey, the movement and sweat had turned the wool into felt socks.
Felt is a textile material that is produced by matting, condensing, and pressing fibers together. Felt can be made of natural fibers such as wool or animal fur or synthetic fibers such as petroleum-based acrylic or acrylonitrile, or wood-based rayon. Blended fibers are also common. Felt has special properties that allow it to be used for a wide variety of purposes. It is fire-retardant and self-extinguishing; it dampens vibration and absorbs sound, and it can hold large amounts of fluid without feeling wet.
Felt from wool is considered to be the oldest known textile. Many cultures have legends as to the origins of felt making. Sumerian legend claims that Urnamman of Lagash discovered the secret of felt making. The stories of Saint Clement and Saint Christopher relate that the men packed their sandals with wool to prevent blisters while fleeing from persecution. At the end of their journeys, the movement and sweat had turned the wool into felt socks.
Today’s pressed wool felt is made via an intricate process often referred to as “wet processing.” Fibers are worked together by applying pressure, moisture, and vibration, then carded and cross-lapped to make multiple material layers. The material’s ultimate thickness and density determine the number of layers that are then steamed, wetted, pressed, and hardened.
In the wet felting process, hot water is applied to layers of animal hairs. Repeated agitation and compression cause the fibers to hook together or weave together into a single fabric piece. Wrapping the properly-arranged fiber in sturdy, textured material such as a bamboo mat or burlap will speed up the felting process. The felted material may be finished by fulling.
Specifications: SAE/C-F-206G
Most fiber used in pressed felt is wool. Wool fibers have small barbs on them, which aid in the natural locking or felting process. The manufacturing of pressed wool felt is primarily mandated by SAE standards. These standards determine the wool content, density, and other physical and mechanical properties of the felt. Pressed wool felt is identified by the SAE standards F-1 thru F-26.
The lower the SAE numbers will be more machinable, have better vibration absorption, and have better abrasion resistance. Wool felt has excellent wicking properties. It can absorb its weight in oil several times, and when used as a lubrication wick, it will supply small amounts of oil at a uniform rate. Pressed wool felt has excellent solvent resistance and stability in oil. SAE wool felt is unaffected by sunlight and maintains its original form after long periods of stress.
COMMON TYPES:
- Wool
- Polyester
- High Temperature
COMMON TRADE NAMES:
- NOMEX
APPLICATIONS:
- Gaskets
- Wicking
- Dust Shields
- Grease Retainer
- Sound Reduction
- Wipers
- Weather Stripping
- Pads

| Type 1 Roll Felt SAE No. | F-1 | F-2 | F-3 | F-5 | F-7 | F-10 | F-11 |
| Classification No. | 16R1 | 16R2 | 16R3 | 12R1 | 12R3 | 9R1 | 9R2 |
| Wool Content % | 95 | 90 | 85 | 95 | 80 | 95 | 87 |
| Chlorothene Solubles % | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 4.0 | 2.5 | 3.0 |
| Water Solubles % | 2.5 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 4.0 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| Total Solubles % | 3.0 | 4.0 | 4.5 | 3.0 | 7.0 | 3.0 | 4.5 |
| Ash Content % | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 3.0 |
| Tensile Strength psi | 500 | 500 | 400 | 250 | 225 | 200 | 75 |
| Slit Resistance psi | 33 | 28 | 22 | 18 | 12 | 8 | 6 |
| Width (inch) | 60 | 60 | 60/72 | 60 | 72 | 72 | 72 |
| Color | White | Pink | Gray | White | Gray | White | Gray |
| Type1 Roll Felt SAE No. | F-13 | F-15N | F-26N | F-50 | F-51 | F-55 |
| Classification No. | 9R4 | 9R5 | 8R5 | 16R1X | 16R3X | 12R3X |
| Wool Content % | 75 | 55 | 45 | 95 | 92 | 75 |
| Chlorothene Solubles % | 4.0 | 4.0 | 8.0 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 4.0 |
| Water Solubles % | 4.0 | 5.0 | 6.0 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 4.0 |
| Total Solubles % | 8.0 | 9.0 | 14.0 | 3.0 | 4.5 | 8.0 |
| Ash Content % | 3.5 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 3.0 |
| Tensile Strength psi | 75 | 75 | 75 | 500 | 300 | 200 |
| Slit Resistance psi | 2 | 2 | 2 | 33 | 22 | 12 |
| 72 | 72 | 72 | 72 | 60 | 60/72 | 72 |
| Color | Gray | Gray | Gray | White | Gray | Gray or Black |
FELT / POLYESTER
POLYESTER FELT IS A SYNTHETIC, NEEDLE-PUNCHED FELT MADE FROM POLYESTER FIBERS.
Material is normally supplied in either black or white. This general-purpose felt is made in various densities with thicknesses ranging from .019” to 2”.
Polyester felt is fairly inexpensive and often made in comparable density and thickness to SAE-pressed wool felt. The maximum temperature of polyester felt is 300°F, compared to 200°F for SAE-pressed felts. This material is commonly used for filtration applications, gaskets, wipers, and padding in various industries. The density of polyester felt is commonly measured in ounces per sq. yd.
Polyester felt is normally supplied in either black or white, in various densities and thicknesses ranging from .019” to 2.0”.
APPLICATIONS:
- Filtration
- Gaskets
- Weatherstripping
- Wipers
- Crate lining
- Padding

To learn more about felt in wool or polyester material from The Gund Company or request a quote for your application, Contact Us Today!


